The rising utility costs – especially for electricity obtained in the traditional manner – raise the importance of efficiency in the use of these resources. How to optimize the expenses and costs that are necessary in the context of production activities? The key issue is not only the analysis of the data itself, but also the way in which it is obtained.
Utilities are most commonly associated with electricity, but these resources need to be considered more broadly and also include, e.g. water, gas. They are used every day in every factory in the world as production without access to them would often be impossible. It is therefore a natural, even standard cost. And perhaps that is why – a common mistake – it is often not taken into account when calculating the cost of producing a given item.
Meanwhile, a common direction pursued by factories seeking to balance production and environmental effect is to optimize utility usage. This translates not only into ecology, but also has a tangible financial dimension.
It turns out that utility expenses are often – when viewed through the prism of reporting and analytics – invisible. They are simply recognized as a fixed cost of business and, therefore, are not subject to cost-effectiveness assessment. Many entities go even further: they estimate utility costs without a thorough understanding of how these expenses vary between production lines. Worse still, there is often not even a thought given to how they affect in practice the effectiveness of operating equipment, or OEE – a format that should be an important parameter for any type of business. In this context, it is worth remembering one of the basic principles of Lean Manufacturing – it is not possible to manage effectively something that is not measured. In this light, media management is in fact the foundation of any activity.
Standard problems with costly utilities
Regardless of the type of business of a given factory, manufacturing means the same challenges in terms of utilities. These are:
- high utility expenses and a lack of ideas on how to reduce costs,
- only general knowledge of the products; no information on how much energy – and on which units or machines – is consumed,
- acceptance of use losses – being passive about the fact that machinery or equipment is on standby or running while consuming energy with no productive effect,
- ignorance of media wastage phenomena; e.g. careless attitude towards potential leaks and losses,
- no utility control: lack of planning in terms of, for example, energy and its use.
How to reduce utility costs in the production process?
The solution to all the cost optimization problems outlined above is a utility control system. How does the 能源管理系统 solution implemented by ANT work in this context?
It provides a complete utility control system by using technology to connect all critical components. These include meters and sensors for real-time data monitoring. This includes utilities such as:

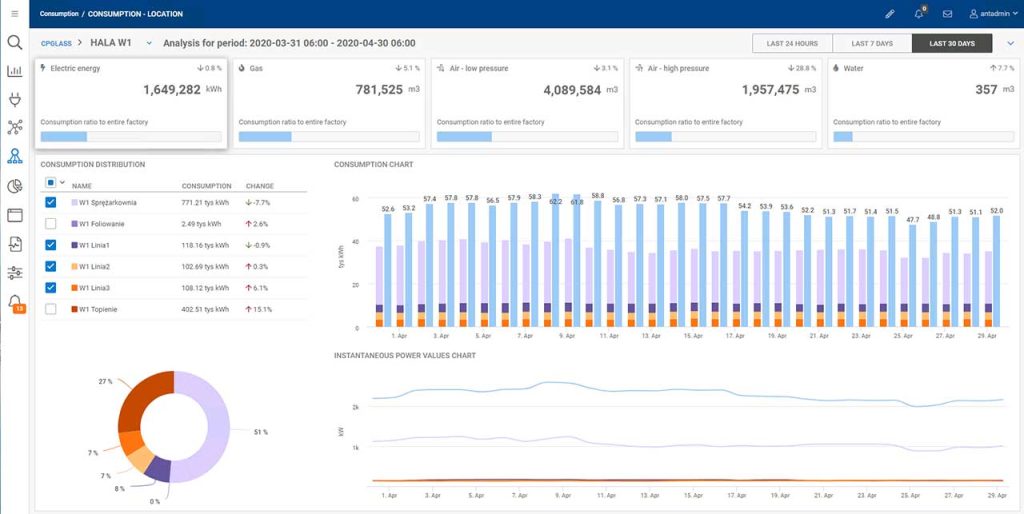
Each utility is monitored on the basis of dozens of well-defined parameters. At the same time, the flexibility of the monitoring itself is evident. It takes place at different levels. In this way, it is possible to effectively separate a given factory from, for example, a specific department, room, process line or specific machine.
It is of crucial importance in the context of optimization to correlate the generated utility consumption data with the information packages of the production itself. This makes conversion analysis easier: the system shows an accurate picture of total production and non-production costs. The result is the ability to easily calculate the cost of utility consumption and the cost per unit of product.
The precision of the data and its extent and level of detail translate into easy forecasting of utility consumption and costs based on the production plan. Reporting also facilitates the acquisition of information on losses occurring during non-productive times – for example, the detection of leaks and technical anomalies that affect production efficiency. An interesting option in this context is the Power Guard system, which alerts you if the amount of electricity ordered is exceeded.
What are the benefits of implementing a monitoring system?
The main advantage is, of course, more efficient management of consumption – instead of taking it as a fixed cost with no possibility of control, the management has full opportunity to verify costs and effects. Implementation can also be looked at in terms of benefits, such as:
- much faster access to aggregated and detailed data
- comprehensive real-time information on utility consumption
- savings that can result from the absence of penalties for exceeding capacity
- reduced production costs and improved quality of order processing
- faster and more precise identification of failures and disruptions
- an extensive system of alerts, notifications and reports
- paying attention to the issue of environmental protection: increasing awareness of the CO2 footprint
How do the changes look in practice?
Based on the experience of companies that have already implemented utility monitoring systems, it can be concluded that better management of highly fluctuating costs – e.g. electricity, water, gas – translates into higher productivity and profits of these companies. Here are some examples of the benefits:
• utility consumption reduced by 5-15%
• 10% savings on utility costs
• power consumption reduced by approx. 20%
In addition to better budgeting and more efficient cost calculations, it is worth remembering about government programs – depending on the country, you can count on support and tax incentives that reach up to tens of thousands of euros.
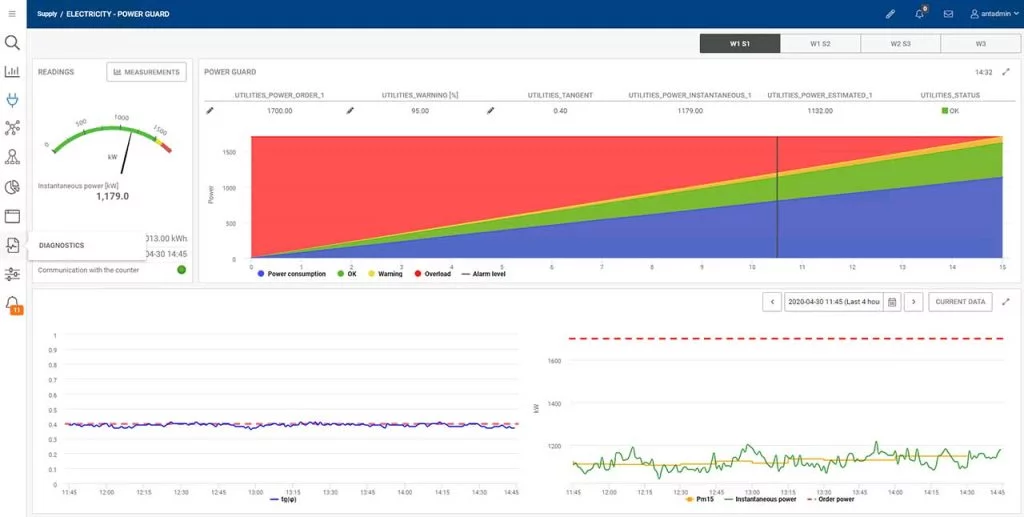
Its major advantage is comprehensive diagnostics covering specific areas of loss. In this way, it is easier to determine trends in utility consumption in terms of specific time intervals – days, weeks, seasonal and operational periods. This translates into better decisions, which are based on real-time data.



