-
- Optimised Production and Quality: PPM ensures consistent control over manufacturing processes, leading to improved product quality, reduced downtime, and operational efficiency.
- Comprehensive Data Management: PPM systems offer real-time monitoring, recipe management, and detailed logging, allowing for full traceability, quick recovery from failures, and better compliance with regulations.
- Scalability and Security: Designed for future growth, PPM systems integrate easily with new equipment, offer secure access controls, and ensure data is protected through backups and role-based user management.
1. Introduction to Process Parameters Management (PPM)
Process Parameters Management (PPM) is a critical system in modern manufacturing, designed to manage, control, and optimise production processes by maintaining the correct settings of process parameters across multiple machines. In a manufacturing environment, consistency is key to maintaining product quality, meeting regulatory standards, and ensuring operational efficiency. PPM systems are used to automate and synchronise the management of these parameters, enabling manufacturers to handle complex production lines with minimal manual intervention.
A PPM system is often integrated across a network of manufacturing equipment, enabling real-time control, monitoring, and reporting of parameters such as temperature, pressure, time, and machine-specific settings. By doing so, it helps manufacturers prevent errors, reduce downtime, and increase productivity.
2. Key Benefits of Implementing PPM in Manufacturing
The implementation of a robust PPM system offers several advantages for manufacturing operations, including:
-
- Consistency in Product Quality: By controlling and monitoring key process parameters, manufacturers can ensure the quality and uniformity of products. PPM systems enable quick identification and correction of any deviations from predefined settings.
-
- Operative Effizienz: Automating the control of process parameters reduces the need for manual adjustments, saving time and reducing the risk of human error. Additionally, PPM systems optimise production by synchronising machine settings, ensuring smoother workflows and better utilisation of equipment.
-
- Improved Compliance and Traceability: Modern PPM systems log all changes to parameters, ensuring full traceability. This is particularly important in industries where regulatory compliance is a key concern. Detailed logs allow for quick identification of the root cause in case of any issues during production.
-
- Reduced Downtime: PPM systems are designed to quickly restore settings and parameters after equipment failure, minimising production interruptions and ensuring quicker recovery.
- Skalierbarkeit: PPM systems can easily be extended to accommodate new equipment or production lines, ensuring that future expansions do not disrupt existing operations.
3. Core Features of an Effective PPM System
An effective PPM system incorporates several key features, including:
-
- Centralised Recipe Management: The system stores a central repository of process recipes, which are essentially predefined sets of values for all parameters required to run specific machines or product lines. This ensures consistency and accuracy across different batches or shifts.
-
- Real-Time Monitoring: The system provides real-time monitoring of parameters across multiple machines, allowing operators to detect and correct issues immediately. Monitoring includes tracking deviations, identifying performance bottlenecks, and ensuring smooth process flows.
-
- User Access Control: Access to the system is managed through strict role-based authorisation, ensuring that only authorised personnel can make critical changes to the process parameters.
-
- Data Logging and Reporting: Comprehensive logging of system events, parameter changes, and user activities ensures full traceability. PPM systems often include built-in reporting tools that allow operators to generate reports on production performance, recipe changes, and other key metrics.
- Extensibility: PPM systems are designed to scale horizontally, meaning they can integrate additional machines or production lines with minimal disruption to existing workflows.
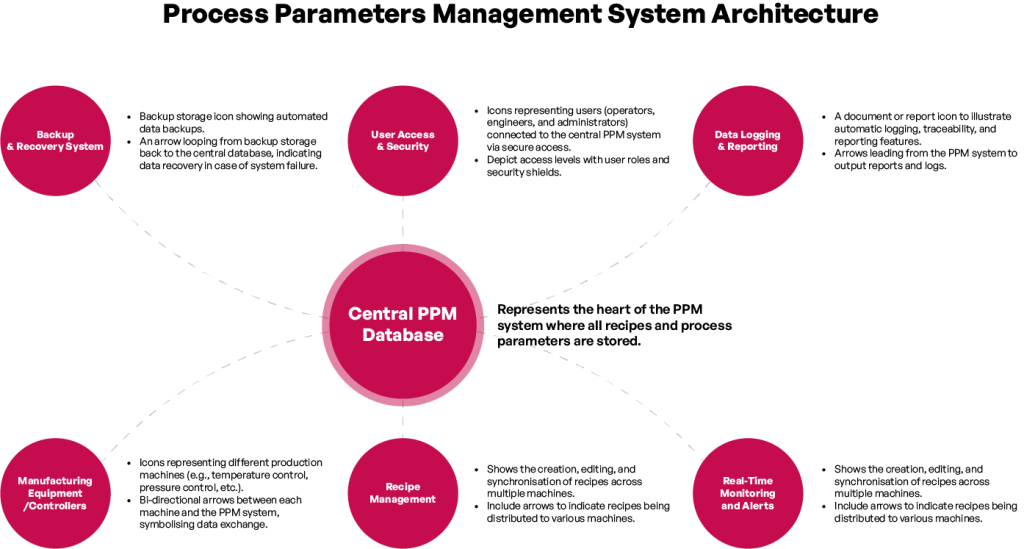
4. PPM System Architecture and Integration
A well-designed PPM system is typically based on a modular architecture that allows for easy integration with different types of production equipment. The system communicates with machine controllers through secure protocols and APIs, allowing it to send and receive data between machines and a centralised database.
The architecture of a PPM system is often built with vertical and horizontal scalability in mind. Vertical scaling ensures that the system can handle increased data loads as the production scale grows. Horizontal scaling enables the addition of new equipment or production lines without affecting the performance of the overall system.
Additionally, a robust PPM system operates entirely within the internal network of a manufacturing site, ensuring that data remains secure and isolated from external systems. Integration with manufacturing equipment requires careful attention to communication protocols, such as OPC servers, to ensure seamless data exchange.
5. User Management and Security in PPM
User management in a PPM system is vital for ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorised access. The system should support multiple levels of user access, allowing only approved personnel to make changes to process parameters or access sensitive data.
The system integrates with central authentication services, such as Active Directory, to ensure that user credentials and permissions are managed securely. For equipment-level access, internal authentication mechanisms are employed to prevent unauthorised modifications to the machine settings.
Moreover, the system should allow for role-based access control, defining user roles such as operator, engineer, and administrator, each with different permissions for interacting with the system. Regular audits of user activity and permissions help to maintain security and accountability.
6. Data Handling, Backup, and Recovery in PPM
Data handling in a PPM system is a critical aspect that ensures the system’s reliability and continuity. The system must be capable of backing up process parameters, machine settings, and system logs regularly to prevent data loss.
In the event of a system failure, the PPM system should include procedures for rapid recovery, typically within an hour. Automated backups should cover both the database and middleware services, ensuring that the system can be restored to its previous state without significant data loss.
Regular backups also allow manufacturers to archive historical data, which can be useful for compliance audits, performance reviews, or troubleshooting.
7. Recipe Management and Synchronisation in PPM
At the core of a PPM system is its ability to manage and synchronise recipes. A recipe in the PPM context refers to a collection of process parameters that define how a specific machine or production line should operate for a particular product.
The PPM system allows engineers to create, copy, and edit recipes, ensuring that production processes are consistent. The system also supports defining ranges of acceptable parameter values, preventing the use of improper settings.
A significant feature of the system is its ability to synchronise recipes across multiple machines. When a recipe is updated in the central database, the changes are automatically reflected in all relevant equipment, ensuring that every machine operates according to the latest specifications.
8. Monitoring, Logging, and Reporting in PPM
A PPM system continuously monitors all process parameters, generating real-time alerts if any parameter deviates from its defined range. These alerts allow operators to take corrective actions quickly, minimising the risk of defects or equipment damage.
The system logs every event, including parameter changes, system errors, and user activities. These logs are timestamped and stored securely, providing a full history of changes for traceability. The system also allows users to generate detailed reports, filtering data by machine, recipe, product number, and time range.
Reports can be exported in formats such as Excel or CSV, enabling easy sharing and analysis of production data.
9. Best Practices for Implementing and Scaling PPM
To maximise the benefits of a PPM system, manufacturers should follow these best practices:
-
- Customise the System for Your Needs: Tailor the PPM system to the specific machines and processes used in your facility, ensuring that it addresses the unique requirements of your production environment.
-
- Regular Updates and Audits: Keep the system up to date with the latest software and security patches, and regularly audit system performance to ensure it continues to meet operational needs.
-
- Train Personnel: Provide comprehensive training for all system users, from operators to engineers, ensuring they understand how to use the system effectively and troubleshoot common issues.
-
- Plan for Scalability: Design the system architecture with future growth in mind, ensuring that new equipment can be added seamlessly without disrupting existing processes.
10. Conclusion
Process Parameters Management (PPM) is an essential tool for modern manufacturing, providing the control and visibility necessary to maintain high standards of quality, efficiency, and compliance. By centralising the management of process parameters and ensuring real-time monitoring and reporting, PPM systems help manufacturers optimise their operations, reduce downtime, and scale production with ease. Implementing a PPM system tailored to your facility’s needs will not only improve product quality but also ensure operational resilience in an increasingly competitive market.
The main three key benefits of Process Parameters Management (PPM) are:

Enhanced Product Quality
PPM ensures that process parameters are consistently controlled, leading to uniformity in product quality and reducing defects across production lines.
Operative Effizienz
By automating the control and monitoring of process parameters, PPM reduces manual interventions, minimizing human error and downtime, and streamlining production processes.

Improved Traceability and Compliance
PPM systems provide detailed logs and reports, ensuring full traceability of changes and compliance with industry standards, helping manufacturers meet regulatory requirements.
Mehr Einblicke erhalten

Wie unterstützt ANT Smart Factory die schlanke Produktion?
Lean Manufacturing ist ein Produktionsprozess, der auf dem Konzept der Maximierung der Produktivität bei gleichzeitiger Minimierung der Verschwendung in der Fertigung basiert. Im Verlauf dieses Prozesses

Integration aller Produktionsprozesse - entdecken Sie die Möglichkeiten der Smart Factory
Die Smart Factory erfüllt die Ziele der Industrie 4.0 durch die Rückverfolgbarkeit und Kommunizierbarkeit von Objekten, die Vernetzung von Maschinen und Anlagen sowie die

Wie kann man eine Strategie zur Entwicklung einer digitalen Fabrik entwickeln?
Bewerten Sie Ihren derzeitigen Digitalisierungsgrad: Das ist wichtig, denn so können Sie feststellen, welche Bereiche am meisten verbessert werden müssen und wie viel Arbeit nötig ist.

