- Manufacturing data analytics involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources (EMS, MES, ERP) to optimize operations, improve product quality, and drive growth. Key areas of focus include performance, material consumption, costs, and comparative analysis.
- Data analysis techniques such as correlational analysis, hypothesis testing, and AI are used to uncover insights, identify bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and reduce costs.
- Benefits of data analytics include improved operational efficiency, enhanced product quality, optimized resource utilization, cost reduction, risk mitigation, and innovation.
- Manufacturing data analytics involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources (EMS, MES, ERP) to optimize operations, improve product quality, and drive growth. Key areas of focus include performance, material consumption, costs, and comparative analysis.
Manufacturing Data Analytics: Unlocking Insights with an Enterprise Data Platform
Manufacturing is undergoing a digital transformation, fueled by the vast amounts of data generated across the production process through systems like EMS, MES, ERP, or other data sources. To harness the full potential of this data, organizations are increasingly adopting Enterprise Data Platforms (EDPs). By centralizing and analyzing data from diverse sources, manufacturers can gain valuable insights to optimize operations, improve product quality, and drive growth. Common analytics tools include Power BI, Dataiku, or Plotly.
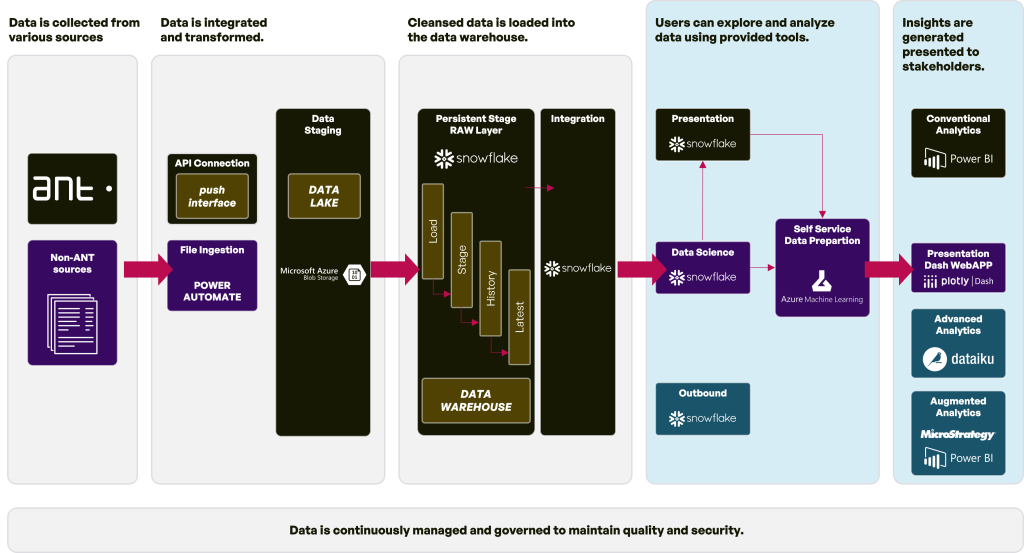
What manufacturing comapnies tend to monitor?
Manufacturing organizations often focus their analytics efforts on key performance indicators (KPIs) that directly impact their bottom line.
Core areas of monitoring include:
-
- Leistung: Metrics such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), production output, and cycle times are essential for assessing operational efficiency.
-
- Material Consumption: Tracking raw material usage, waste generation, and inventory levels helps optimize resource utilization.
-
- Costs: Analyzing production costs, energy consumption, and labor expenses is crucial for cost management.
-
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing performance across different production sites or product lines provides valuable benchmarks.
-
- Strategic Impact: Evaluating the effectiveness of various initiatives and strategies helps refine business decisions.
-
- UX Changes: Ease of changes in the interface possibility of independent modifications and creation of various variants.
Why do goods producers need to analyse collected data?
The overarching goal of manufacturing data analytics is to gain a comprehensive understanding of operations and identify areas for improvement. Key objectives include:
-
- Standardized Data Access: Consolidating data from diverse sources into a single platform facilitates analysis and reporting.
-
- ROI Measurement: Tracking the impact of initiatives on targeted KPIs enables evaluation of their effectiveness.
-
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging insights from data to optimize processes, reduce costs, and improve quality.
-
- Performance Benchmarking: Comparing performance against industry standards or internal targets drives continuous improvement.
-
- Operative Effizienz: Identifying bottlenecks, optimizing production schedules, and reducing downtime.
What kind of data manufacturers use to analyse production?
Effective data analytics relies on a robust data foundation. Manufacturers collect data from various sources, including:
-
- Production Equipment: Machine performance, downtime, and maintenance records.
-
- Utilities: Energy consumption, water usage, and waste disposal data.
-
- Qualitätskontrolle: Defect rates, rework, and material rejection information.
-
- Cost Management: Financial data, labor costs, and material prices.
-
- Human Resources: Employee attendance, overtime, and skill sets.
Both aggregated data (summaries, KPIs) and granular historical data are essential for comprehensive analysis.
What kind of data compilations do manufacturers do and what statistical methods do producers use?
To uncover valuable insights, manufacturers employ a range of data analysis techniques:
-
- Correlational Analysis: Identifying relationships between different variables to understand their impact.
-
- Hypothesis Testing: Verifying assumptions about data patterns to support decision-making.
-
- Big Data and AI: Leveraging advanced technologies for complex data analysis and predictive modeling.
-
- Experimental Analysis: Using data to test new ideas and strategies.
While simple correlations often serve as a starting point, the industry is increasingly adopting sophisticated statistical methods and AI-driven approaches.
What is the outcome of manufacturing data analysis?
The outcomes of manufacturing data analytics are far-reaching and can significantly impact business performance. Key benefits include:
-
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Identifying bottlenecks, optimizing production schedules, and reducing downtime.
- Example: A manufacturing plant analyzes machine downtime data to identify recurring issues, leading to targeted maintenance interventions that reduce equipment failures by 20%.
-
- Enhanced Product Quality: Detecting quality issues early in the process and implementing corrective actions.
- Example: A quality control department uses data analytics to identify patterns in defect rates, leading to process adjustments that reduce defects by 30%.
-
- Optimized Resource Utilization: Allocating resources effectively based on data-driven insights.
- Example: Analyzing energy consumption patterns helps a manufacturing plant identify opportunities for energy efficiency, resulting in a 10% reduction in energy costs.
-
- Cost Reduction: Identifying cost-saving opportunities through process optimization and waste reduction.
- Example: Identifying and eliminating waste through data analysis leads to a 5% reduction in production costs.
-
- Risk Mitigation: Predicting potential issues and taking proactive measures.
- Example: Analyzing supply chain data helps a company identify potential disruptions and develop contingency plans, reducing supply chain risks.
-
- Innovation: Using data to develop new products and processes.
- Example: Analyzing customer data helps a company identify new product opportunities, leading to the development of successful new product lines.
By harnessing the power of data analytics, manufacturers can gain a competitive edge and drive sustainable growth.
Mehr Einblicke erhalten

Data Warehouse vs. Data Lake, was sind die Unterschiede?
Data Lakes and Data Warehouses: Cornerstones of Modern Manufacturing The manufacturing industry is undergoing a data revolution. With advancements in technology, factories are generating unprecedented

Analyse von Fertigungsdaten - Erschließung von Erkenntnissen mit einer Unternehmensdatenplattform
Manufacturing Data Analytics: Unlocking Insights with an Enterprise Data Platform Manufacturing is undergoing a digital transformation, fueled by the vast amounts of data generated across

Methoden der Datenintegration und -aufbereitung in einer Fabrikumgebung
Daten sind der Schlüssel In der verarbeitenden Industrie werden Daten aus einer Vielzahl von Quellen generiert, darunter Produktionsanlagen, Sensoren, ERP-Systeme und Qualitätskontrollen.

