1. The Importance of Production Sustainability
In today’s world, where environmental concerns and economic challenges intertwine, the importance of sustainable production patterns and practices cannot be overstated. The concept of sustainability in production is no longer a luxury but a necessity. As we face the escalating pressures of climate change, resource depletion, and a heightened consumer demand for environmentally conscious products, countries and businesses are compelled to reevaluate their production processes.
Sustainable production is not merely about reducing the environmental footprint of manufacturing activities. It’s a holistic approach that balances ecological responsibility with economic growth, viability and social equity. Embracing sustainable practices allows companies to future-proof their operations, ensuring long-term viability in a market that increasingly values ethical and eco-friendly practices.
The Role of Energy Management Systems (EMS) in Enhancing Production Sustainability
In the quest for sustainable production, Energy Management Systems (EMS) emerge as critical tools. These systems represent a fusion of technology, practices, and strategies designed to manage, monitor, and conserve energy in a manufacturing or production facility. The implementation of an EMS can be transformative, leading to significant enhancements in energy efficiency, cost reductions, and environmental stewardship.
EMS serves as a cornerstone for companies seeking to embrace sustainability in their own production systems manufactured products, and processes. By offering real-time data and insights on energy consumption, these systems enable businesses to make informed decisions that align with sustainability goals. This includes identifying energy-intensive areas, optimising machine usage, and reducing wastage. The ripple effect of these changes is profound, leading to cost savings, reduced carbon emissions, and improved operational efficiency.
Moreover, EMS aligns with global sustainability trends and regulatory requirements, helping businesses stay ahead in a competitive and evolving marketplace. They play a pivotal role in developing countries achieving certifications such as ISO 50001, which further cements a company’s commitment to energy efficiency and environmental stewardship.

2. Understanding Production Sustainability
Defining Production Sustainability
Production sustainability, at its core, is about creating goods and services using processes that are non-detrimental to the environment, economically viable, and socially responsible. It’s a multifaceted concept that involves minimising the ecological impact of production while ensuring that operations are financially sound and socially equitable. This involves efficient utilisation of resources, reducing waste, recycling materials, and minimising emissions and pollutants. The goal is to create a production life cycle that can be maintained indefinitely without depleting natural resources, pollution, or harming the ecosystem.
The Benefits of Production Sustainability
The benefits of adopting sustainable production practices are manifold. Firstly, it is sustainable consumption leads to a significant reduction in operational costs over time. Energy-efficient manufacturing processes and waste reduction strategies decrease utility bills and material costs. Secondly, sustainable production enhances a company’s brand image and reputation. Consumers are increasingly drawn to brands that demonstrate environmental responsibility, which can lead to increased customer loyalty and market share. Thirdly, it ensures compliance with environmental regulations, avoiding fines and legal issues. Lastly, sustainable practices can lead to innovation, as companies are often required to rethink and redesign their production processes, leading to more efficient and effective methods of manufacturing.
Challenges to Achieving Production Sustainability
Despite its numerous benefits, achieving production sustainability is not without its challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the initial cost and investment required to transition to more sustainable practices. Retrofitting factories with energy-efficient equipment or investing in renewable energy sources can be costly upfront, though they offer long-term savings. Another challenge is the lack of expertise and knowledge in implementing more sustainable products and practices. This includes understanding the complexities of sustainable materials, energy-efficient technologies, environmental degradation, and waste minimisation techniques. Additionally, companies often face resistance to change, whether from internal stakeholders or from a supply chain entrenched in traditional practices. Overcoming these barriers requires a clear vision, committed leadership, and a willingness to invest in the future.
3. Energy Management Systems (EMS)
What is EMS?
Energy Management Systems (EMS) are a pivotal component in the modern industrial landscape, designed to optimize energy use and improve sustainability. These systems encompass a range of technologies and processes aimed at monitoring, controlling, and conserving energy within a facility. At their core, EMS is composed of hardware and software that collect data from various energy-consuming sources, like machinery and lighting systems. They utilise sophisticated algorithms to analyse this data, providing insights into energy usage patterns and identifying areas for improvement. The integration of EMS allows facilities to transition from passive energy consumption to active energy management, leading to significant enhancements in efficiency and sustainability.
The Different Types of EMS
EMS can be categorised into several types, each catering to different needs and scales of operation:
- Industrial EMS: Designed for large-scale industrial settings, these systems are robust and complex, offering detailed analytics and control over extensive manufacturing operations.
- Building EMS: These are used in commercial buildings to manage HVAC, lighting, and other energy-consuming systems, focusing on comfort and efficiency.
- Home EMS: Tailored for residential use, these systems help homeowners monitor and reduce their energy consumption through user-friendly interfaces.
- Grid EMS: Operating at a macro level, these systems manage the energy flow within electrical grids, ensuring stability and efficiency in energy distribution.

The Benefits of Implementing an EMS
The implementation of an EMS brings numerous benefits, making it an invaluable tool for sustainable management and production sustainability:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: EMS provides real-time data and analytics, enabling businesses to identify and rectify inefficient energy use.
- Cost Savings: By optimising energy use, companies can significantly reduce their utility bills, leading to long-term financial benefits.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: EMS helps in streamlining operations by identifying the most energy-efficient ways to run production processes.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced energy consumption directly translates to lower carbon emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
- Compliance and Reporting: EMS assists in adhering to energy regulations and standards, such as ISO 50001, and simplify the process of reporting for compliance purposes.
- Data-Driven Decisions: The insights provided by EMS enable informed decision-making, allowing managers to base their strategies on accurate and timely data.
- Predictive Maintenance: By monitoring equipment performance, EMS can predict potential failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
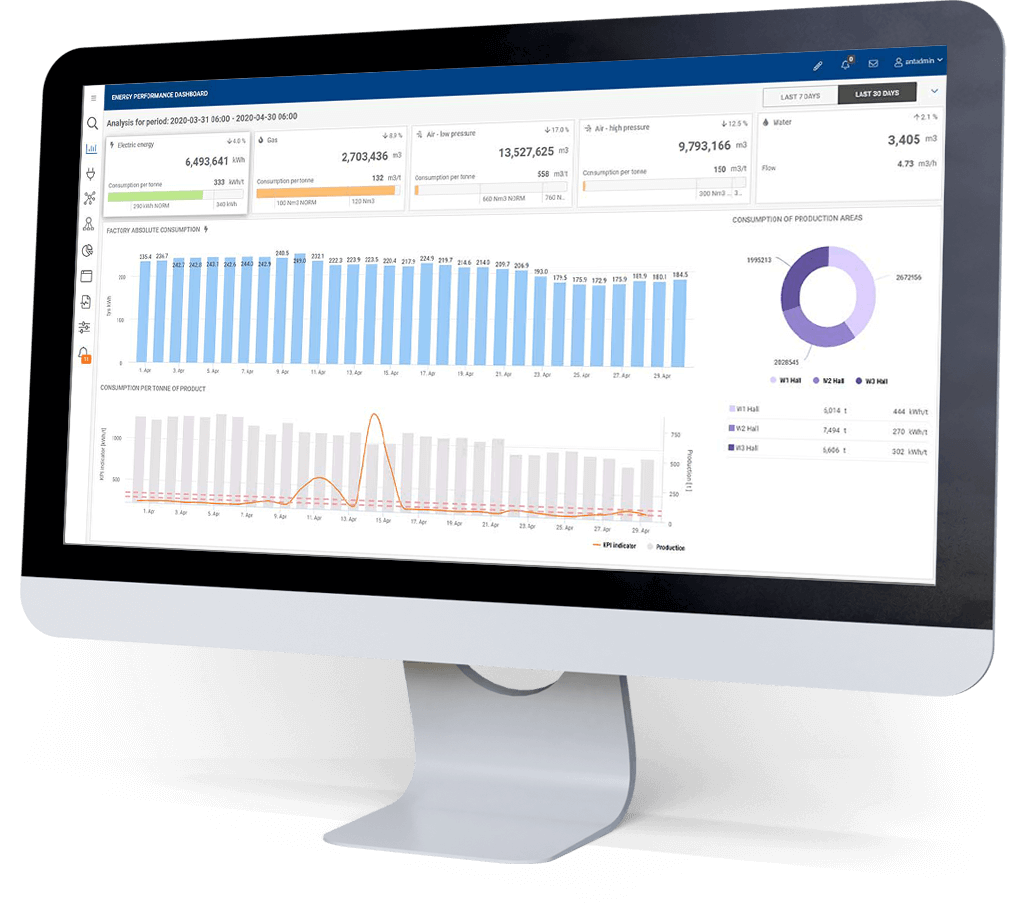
4. Implementing an EMS for Production Sustainability
The Steps Involved in Implementing an EMS
Implementing an Energy Management System (EMS) is a strategic process that requires careful planning and execution. The following steps outline the typical pathway for successful EMS implementation:
- Assessment and Planning: The first step involves conducting a thorough energy audit to assess current energy consumption patterns and identify areas for improvement. This phase also includes setting clear objectives and outlining the scope of the EMS implementation.
- Selection of the Right System: Based on the assessment, companies should choose an EMS that best fits their specific needs. This involves considering factors like the size of the operation, the type of industry, and specific energy goals.
- Installation and Integration: The selected EMS is then installed and integrated into the existing infrastructure. This step might require retrofitting older equipment or introducing new technologies.
- Staff Training: A critical aspect of successful implementation is ensuring that staff are adequately trained to use the EMS. Training helps employees understand the system’s functionality and how to interpret the data it provides.
- Monitoring and Fine-Tuning: Once the EMS is operational, continuous monitoring is essential. This allows for the fine-tuning of the system to ensure optimal performance.
- Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Finally, gathering feedback from the system and users helps in making iterative improvements, ensuring the EMS remains effective and efficient over time.
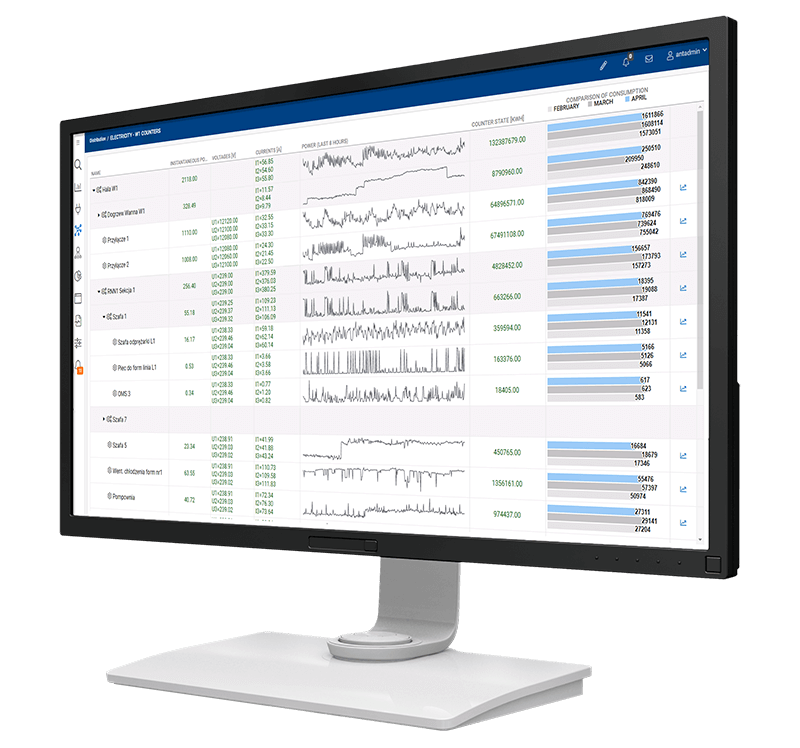
The Challenges of Implementing an EMS
While the benefits of an EMS are clear, the implementation process can pose several challenges:
- High Initial Cost: The initial investment in an EMS can be substantial, covering hardware, software, and training costs.
- Technical Complexity: Implementing an EMS can be technically challenging, requiring specialised knowledge and expertise.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating a new EMS with existing infrastructure and processes can be complex and time-consuming.
- Organisational Resistance: Change can often be met with resistance. Gaining buy-in from all levels of the organisation is crucial for successful implementation.
Strategies for Overcoming Implementation Challenges
To overcome these challenges, companies can adopt the following strategies:
- Phased Implementation: Implementing the EMS in phases can help manage costs and technical complexity, allowing for gradual integration and adoption.
- Employee Engagement: Involving employees in the process and providing comprehensive training can help mitigate resistance and ensure smooth implementation.
- Expert Partnerships: Collaborating with experienced vendors or consultants can provide the necessary expertise and support, particularly in areas where in-house knowledge is lacking.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis can help justify the initial investment by highlighting the long-term savings and benefits.
5. Measuring and Tracking Progress
The Importance of Measuring and Tracking Progress
In the journey towards production sustainability, the implementation of an Energy Management System (EMS) is just the beginning. The critical work of measuring and tracking progress is what truly drives continuous improvement and ensures long-term success. This process involves collecting, analysing, and interpreting data to assess the effectiveness of sustainability initiatives and identify areas for further improvement. Regular monitoring and evaluation help businesses stay aligned with their sustainability goals, adapt to changing circumstances, and make informed decisions.
Key Metrics for Measuring Production Sustainability
Several key metrics are crucial for measuring the impact of an EMS on sustainable development and production sustainability:
- Energy Consumption: This fundamental metric tracks the total energy used by a facility, often broken down by department, production line, or individual machine.
- Energy Intensity: This measures energy consumption relative to output, such as energy per unit of product produced, offering insights into efficiency improvements.
- Carbon Footprint: Tracking the carbon emissions associated with energy consumption is essential for assessing environmental impact.
- Cost Savings: Monitoring reductions in energy costs over time helps quantify the financial benefits of the EMS.
- Operational Efficiency: Metrics such as machine downtime, maintenance costs, and production rates are important for evaluating overall operational improvements.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to energy regulations and standards is crucial, and tracking compliance-related metrics is a key aspect of EMS monitoring.
Tools and Techniques for Measuring and Tracking Progress
To effectively measure and track progress, businesses can utilise a variety of tools and techniques:
- Data Analytics Software: Advanced software solutions can analyse the vast amount of data generated by EMS, providing actionable insights and detailed reports.
- Dashboards and Visualisation Tools: These tools offer a user-friendly interface for monitoring real-time data and long-term trends.
- Benchmarking: Comparing performance against industry benchmarks or previous internal metrics helps in evaluating progress.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Conducting periodic energy audits and system reviews ensures that the EMS is functioning optimally and meeting its intended goals.
- Employee Feedback: Engaging with staff who interact with the EMS daily provides valuable insights into practical improvements and challenges.
Measuring and tracking progress is a vital component of any successful EMS implementation. It not only provides evidence of the benefits and environmental impacts of the system but also guides strategic decision-making and continuous improvement efforts. With the right metrics and tools, businesses can effectively monitor their journey towards production sustainability and achieve their environmental and operational objectives.
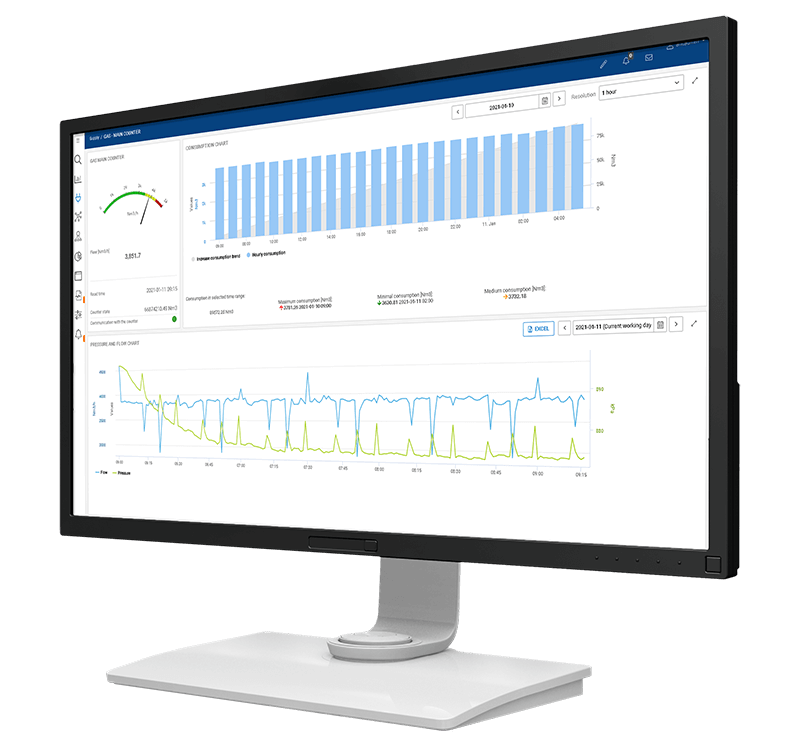
6. Case Studies
Examples of Companies That Have Successfully Implemented EMS to Enhance Production Sustainability
Exploring real-world examples offers valuable insights into the practical application and benefits of Energy Management Systems (EMS) in enhancing production sustainability. One such, life example is a global household appliances manufacturer with a complex network of production facilities.
Case Study: Household Appliances Manufacturer
-
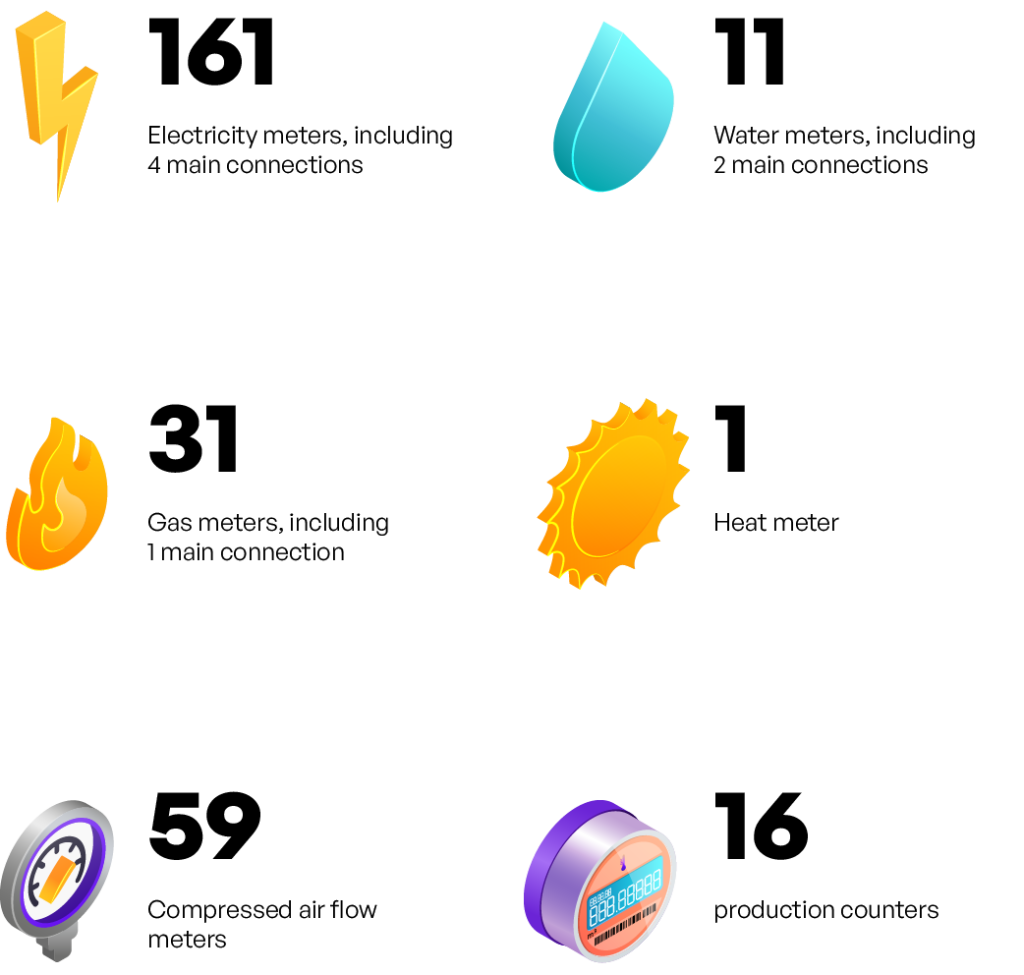
- Overview: This company operates 9 factories, each equipped with an EMS that integrates 75 communication cabinets and 752 measurement devices. These systems collectively monitor 290 virtual meters, processing 8,500 values every minute.
-
- Implementation: The company’s EMS implementation focused on real-time energy monitoring, optimising utility consumption across different departments and production lines. It included features like Power Guards for notifications and alarms, and tools for energy consumption forecasting.
-
- Results: The EMS enabled the company to achieve an 8% reduction in utility usage and a 10% decrease in monthly bills. It also resulted in a 20% reduction in contractual capacity and secured an annual excise duty refund of 60,000 Euros. Key benefits included enhanced efficiency during non-production periods, fault and anomaly detection, and detailed energy consumption analysis.
Lessons Learned from Case Studies
- The success of this case study provides several key lessons:
-
- Comprehensive Monitoring is Crucial: The ability to monitor energy usage in real-time across various metrics was instrumental in identifying savings opportunities.
-
- Customisation and Flexibility: The EMS was tailored to meet the specific needs of different production areas, demonstrating the importance of a flexible and customizable approach.
-
- Employee Engagement and Training: Staff training and involvement were crucial in maximizing the system’s benefits and ensuring its smooth operation.
-
- Long-term Financial Benefits: The significant reductions in energy costs and utility bills highlight the long-term financial benefits of EMS implementation.
-
- Environmental Impact: The reduction in energy consumption directly contributed to lower carbon emissions, underscoring the environmental benefits of sustainable practices.
These case studies not only showcase the tangible benefits of implementing an EMS but also provide practical insights into the strategies and approaches that can lead to successful outcomes. They illustrate the profound impact that EMS can have on production sustainability, both in environmental and economic terms.
Case Study: Glass Containers For Food Industry Manufacturer
Overview: ANT Solutions installed EMS system to reduce cost and achieve better sustainability in Glass Containers Manufacturer in food manufacturer.
Numbers:
- 28 Communication Cabinets
- 280 Measuring devices connected to the ANT EMS System
- 110 Virtual counters
- 4000 Values stored in the database every minute

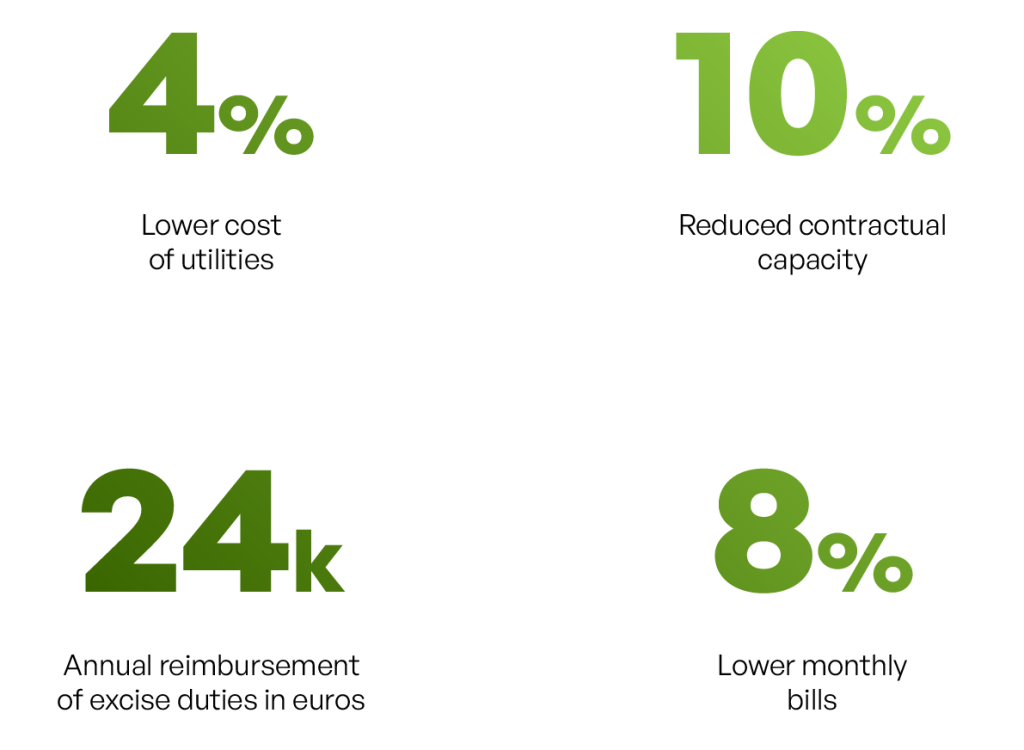
7. Conclusion
The Future of Production Sustainability
As we look towards the future, the importance of production sustainability in the global manufacturing landscape continues to grow. Driven by technological advancements, sustainable lifestyles, increasing environmental awareness, various economic activities and evolving regulatory landscapes, businesses are recognising the imperative to adopt sustainable practices. Energy Management Systems (EMS) stand at the forefront of this transformation, offering a pathway to integrate sustainability into the core of production processes.
The ongoing advancements in EMS technology, including AI and machine learning, are set to further enhance their capabilities. These developments promise more precise energy monitoring, predictive maintenance, and even greater efficiency in resource utilisation. As such, the role of EMS in production sustainability is not just current but increasingly pivotal in the years to the future generations to come.
The Role of EMS in Achieving Production Sustainability Goals
The journey towards sustainability is a continuous process, one that requires commitment, innovation, and the right tools. EMS have emerged as a key enabler in this journey, offering the means to measure, analyse, and optimize energy and resource use elsewhere. They provide a tangible way for businesses to reduce their environmental footprint, improve operational resource efficiency further, and achieve financial savings.
The case studies and examples discussed in this article demonstrate the real-world impact and potential of EMS. They underscore the fact that sustainability is not only about environmental responsibility but also about operational excellence and economic viability. By adopting EMS, companies can align their supply chains and production processes with broader sustainability goals, creating a more resilient and future-proof business model.
In conclusion, enhancing production sustainability is not just an environmental imperative but a strategic business necessity. Energy Management Systems play a critical role in this endeavor, providing the tools and insights necessary to make sustainable production a reality. As we move forward, the integration of EMS in production processes will be a defining factor in the success and sustainability of businesses across the globe.
Related to this article

MES System – Manufacturing Execution System – ANT Solutions
System MES – Manufacturing Execution System 0 % operating time increase 0 % defects quantity reduction 0 % material consumption reduction 0 % changeovers time

Energy Management System (EMS)
Energy Management System (EMS) Monitor utilities usage in real-time and reduce cost Schedule a Demo They Trusted Us: What is ANT EMS? ANT Energy Management

Unlocking Efficiency: 5 Strategies to Optimise Production with Software Solutions
Discover how implementing the right software solutions can revolutionise production optimisation, driving efficiency, and enhancing performance in the factory. Introduction In the modern industrial landscape,

