In today’s world, businesses are increasingly facing pressure to operate in a sustainable and responsible manner. This is not only due to environmental concerns, but also because consumers and investors are increasingly demanding ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) performance from the companies they support.
Energy Management Systems (EMS) can play a critical role in helping businesses achieve ESG excellence. An EMS is a tool that helps businesses identify, monitor, and control their environmental impacts. By implementing an EMS, businesses can reduce their environmental footprint, improve their energy efficiency, and reduce their waste generation.
In this article, we will explore the importance of integrating EMS for ESG excellence in manufacturing. We will also discuss the role of EMS in supporting ESG objectives and company policies in enhancing environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and governance. Additionally, we will provide case studies of successful EMS implementations in manufacturing and discuss the technological advancements that are supporting EMS for ESG goals.
Overview of EMS and ESG in Manufacturing
EMS and ESG are two interconnected concepts that are essential for sustainable manufacturing. EMS provides tools to measure environmental impact of the production, while ESG encompasses the broader environmental, social, and governance responsibilities of businesses.
By integrating Energy Monitoring System into their ESG strategies, manufacturers can:
-
- Improve their environmental performance by reducing their energy consumption, waste generation, and greenhouse gas emissions.
-
- Enhance their social responsibility by ensuring worker safety and health.
-
- Strengthen their governance by adhering to regulations, embracing corporate governance principles, and implementing effective risk management practices.
Importance of Integrating EMS for ESG Excellence
There are several reasons why integrating EMS is essential for ESG excellence in manufacturing:
-
- Regulatory compliance: Many countries have environmental regulations that manufacturers must comply with. An EMS can help businesses identify and comply with these regulations.
-
- Financial benefits: Implementing an EMS can lead to significant cost savings through energy efficiency measures, waste reduction, and improved resource management.
-
- Brand reputation: Consumers and investors are increasingly demanding ESG performance from the companies they support. Implementing an EMS can help businesses improve their brand reputation and attract more customers and investors.
-
- Risk management: An EMS can help businesses identify and mitigate environmental risks, which can protect them from potential liabilities.
-
- Competitive advantage: Manufacturers that are able to demonstrate strong ESG performance can gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
- Competitive advantage: Manufacturers that are able to demonstrate strong ESG performance can gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.

Understanding EMS (Energy Management Systems)
Definition and Key Components
An EMS is a systematic approach to managing energy consumption and optimizing energy efficiency. It provides a framework for businesses to:
-
- Identify and assess their energy consumption patterns.
-
- Develop and implement energy conservation measures and strategies.
-
- Monitor and track their energy performance over time.
-
- Continuously improve their energy management practices and achieve energy savings goals.
The key components of an EMS include:
-
- Energy policy: A formal statement of the company’s commitment to energy efficiency and sustainability.
-
- Energy audit: A comprehensive assessment of the company’s energy consumption patterns, identifying opportunities for energy savings.
-
- Energy objectives and targets: Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for reducing energy consumption and improving energy efficiency.
-
- Energy management program: A detailed plan outlining the actions and strategies to be implemented to achieve the company’s energy objectives and targets.
-
- Energy monitoring and measurement: A system for collecting, analyzing, and reporting on energy consumption data.
-
- Energy management system audit: A regular review of the effectiveness of the EMS, identifying areas for improvement and ensuring ongoing compliance with energy efficiency standards and regulations.
How EMS Fits into the ESG Framework
EMS is an essential component of a comprehensive ESG strategy. It provides a structured approach to managing environmental impacts, which is a critical element of ESG performance. Additionally, EMS can help businesses identify and address social and governance issues related to their environmental impacts.
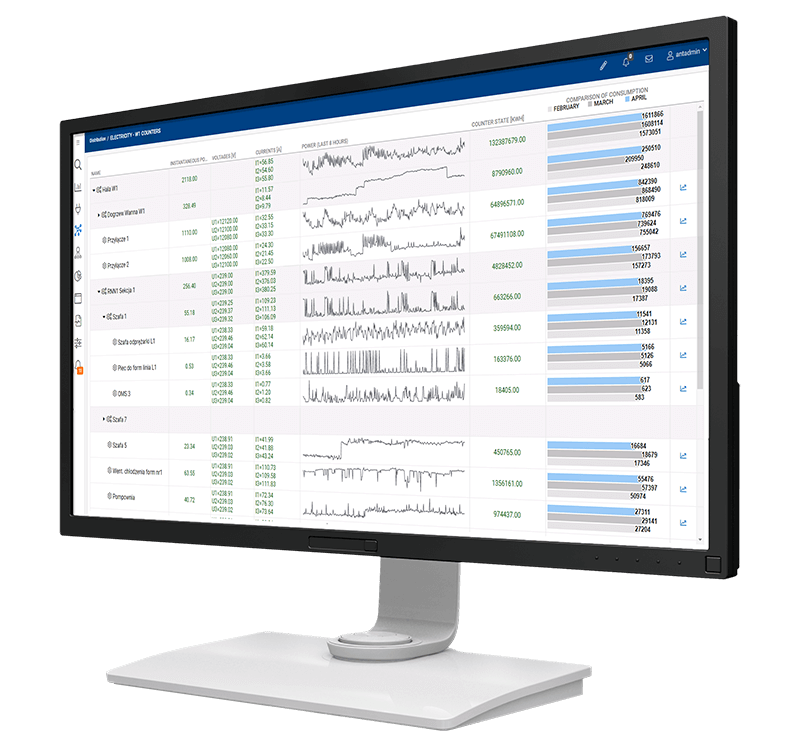
The Role of EMS in Enhancing Environmental Sustainability
EMS can play a significant role in helping businesses achieve environmental sustainability. By implementing an EMS, businesses can:
-
- Reduce their energy consumption: Businesses can identify and implement energy efficiency measures to reduce their energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
-
- Minimize waste generation: Businesses can develop waste reduction programs to minimize waste generation and landfill disposal.
-
- Conserve water: Businesses can implement water conservation measures to reduce their water consumption.
Pollution Prevention and Waste Management
By implementing EMS, businesses can:
-
- Identify and assess their pollution sources.
-
- Develop and implement pollution prevention measures.
-
- Implement a waste management program to reduce waste generation, promote recycling, and ensure proper disposal of hazardous waste.
Energy Efficiency and Carbon Footprint Reduction
EMS improves factories energy efficiency and reduce their carbon footprint:
-
- Conduct energy audits to identify energy-saving opportunities.
-
- Implement energy efficiency measures, such as upgrading lighting and equipment.
-
- Develop and implement renewable energy strategies.
-
- Track and report their greenhouse gas emissions.
Water Management and Conservation
EMS allows businesses conserve water and reduce their water consumption. By implementing EMS, businesses can:
-
- Conduct water audits to identify water-saving opportunities.
-
- Implement water conservation measures, such as fixing leaks and installing water-efficient fixtures.
-
- Develop and implement rainwater harvesting systems.
-
- Track and report their water consumption.
EMS and Social Responsibility in Manufacturing
EMS can also help businesses enhance their social responsibility:
-
- Ensure worker safety and health: Businesses can identify and mitigate workplace hazards, provide safety training to employees, and implement emergency response procedures.
Risk Management and EMS
EMS can help businesses identify, assess, and mitigate environmental risks:
-
- Identify environmental risks through hazard assessments and risk analysis.
-
- Develop and implement risk mitigation plans.
-
- Monitor and track environmental risks.
-
- Report on environmental risks to stakeholders.
Governance and Compliance Through EMS
EMS can also help businesses strengthen their governance and compliance practices. By implementing EMS, businesses can:
-
- Regulatory adherence: Businesses can identify and comply with relevant environmental regulations.
-
- Corporate governance: Businesses can adopt and implement sound corporate governance principles.
-
- Risk management: Businesses can identify, assess, and mitigate environmental risks.
Case Study: Implementation of EMS to support ESG practices in glass containers factory
A glass containers for food industry manufacturer implemented an energy monitoring system to track and analyze its energy consumption. The system was installed in 28 communication cabinets and connected to 280 measuring devices, including electricity meters, gas meters, and compressed air flow meters.
The system collects data on energy consumption every minute and stores it in a database. The data is then used to generate reports that help the manufacturer to identify trends and areas where it can reduce its energy use.
Since implementing the energy monitoring system along with ESG policies, the manufacturer has achieved the following ESG benefits:
-
- Environmental:
-
- Reduced electricity consumption by 4%
-
- Reduced gas consumption by 10%
-
- Reduced water consumption by 8%
-
- Reduced annual CO2 emissions by 24,000 tons
-
- Environmental:
-
- Social:
-
- Improved working conditions by reducing noise and dust levels in the factory
-
- Reduced the risk of accidents and injuries
-
- Social:
-
- Governance:
-
- Improved compliance with environmental regulations
-
- Enhanced corporate image and reputation
-
- Governance:
The energy monitoring system has also helped the manufacturer to save money on its energy bills. The manufacturer estimates that it has saved over €1 million per year in energy costs since implementing the system.
Technological Advancements Supporting EMS for ESG Goals
Technological advancements are playing a key role in supporting EMS for ESG goals. Some of these advancements include:
Automation and IoT in EMS:
-
- Sensors and monitors can collect data on energy consumption, water use, and other environmental metrics in real-time.
-
- Artificial intelligence (AI) can analyze this data to identify trends and opportunities for improvement.
-
- Robotics and automation can be used to automate tasks related to environmental management, such as energy management and waste sorting.
Data Analytics for Environmental Performance Monitoring:
-
- Data analytics tools can be used to track and analyze energy performance data.
-
- This data can be used to identify areas for improvement, measure the effectiveness of EMS initiatives, and make informed decisions about environmental management.
Emerging Technologies in Sustainable Manufacturing:
-
- Blockchain technology can be used to track the provenance of materials and ensure ethical sourcing.
-
- 3D printing can be used to create parts with less material waste.
-
- Artificial intelligence can be used to optimize energy consumption and resource use.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing EMS for ESG in manufacturing companies
Integrating an Energy Management System into a company’s operations can bring numerous advantages to its ESG performance. However, implementing such a system is not without its challenges.
Challenges:
Overcoming Operational and Financial Barriers:
-
- Upfront Investment Costs: Implementing an EMS often necessitates upfront investments in technology, training, and specialized personnel.
-
- Operational Disruptions: The implementation process may temporarily disrupt regular operations, requiring careful planning and communication.
-
- Delayed Return on Investment (ROI): The financial benefits of EMS may not be immediately apparent, necessitating a long-term perspective and a focus on sustainability.
Employee Engagement and Training:
-
- Securing Employee Buy-in: It is crucial to engage employees in the EMS implementation process, fostering a sense of ownership and understanding of its significance.
-
- Effective Training and Communication: Employees need comprehensive training on EMS principles and procedures to ensure proper implementation and utilization.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation:
-
- Dynamic Environment: EMS is an ongoing process that demands continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving technologies, regulations, and market trends.
-
- Flexibility and Change Management: Businesses must be adaptable and willing to modify their practices to optimize energy efficiency and achieve ESG goals.
Solutions:
Businesses can effectively address these challenges by implementing the following strategies:
-
- Conduct a Comprehensive Cost-Benefit Analysis: A thorough assessment of the financial implications of EMS implementation, including potential savings and long-term benefits, is essential.
-
- Early and Consistent Stakeholder Engagement: Actively involve stakeholders, including employees, management, and external partners, throughout the EMS process to ensure alignment and support.
-
- Robust Employee Training and Communication Programs: Develop comprehensive training programs and communication channels to educate employees on EMS principles, procedures, and the importance of energy conservation.
-
- Establish a Continuous Improvement Framework: Implement an ongoing EMS improvement framework that incorporates regular audits, data analysis, and feedback mechanisms to drive continuous optimization.
Benefits of EMS:
Implementing an EMS can yield a range of tangible benefits that contribute to ESG excellence:
-
- Reduced Energy Consumption: EMS enables real-time monitoring and analysis of energy usage, facilitating targeted interventions to reduce consumption and associated costs.
-
- Comprehensive Utility Consumption Overview: EMS provides a holistic view of utility consumption patterns across departments, production lines, and products, enabling informed decision-making.
-
- Predictive Energy Consumption Forecasting: EMS utilizes historical data and advanced algorithms to forecast future energy consumption, enabling proactive planning and resource allocation.
-
- Non-Production Energy Loss Identification: EMS detects and quantifies energy losses during non-production periods, allowing for targeted optimization strategies.
-
- Fault, Leak, and Anomaly Detection: EMS proactively identifies faults, leaks, and anomalies in energy systems, preventing potential equipment failures and energy wastage.
-
- Granular Energy Consumption Analysis: EMS enables detailed energy consumption analysis at the departmental, production line, and product levels, facilitating data-driven energy management decisions.
-
- Government Incentives and Tax Benefits: Governments often provide financial incentives, such as tax breaks, to businesses that implement EMS, recognizing their contribution to energy efficiency goals.
- ISO 50001 Certification Compliance: EMS implementation facilitates compliance with the ISO 50001 energy management standard, demonstrating commitment to energy efficiency and sustainability.

EMS plays a pivotal role in achieving ESG excellence by enabling businesses to optimize energy consumption, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. By implementing comprehensive EMS strategies and overcoming the associated challenges, businesses can enhance their sustainability credentials and contribute to a more energy-efficient future.
Conclusion
Energy Management Systems (EMS) have emerged as a critical tool for manufacturing companies seeking to enhance their ESG performance and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. By providing a comprehensive framework for managing energy consumption, EMS plays a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, optimizing resource utilization, and minimizing environmental impact. Moreover, EMS contributes to ESG excellence by promoting a culture of energy conservation, fostering employee engagement, and strengthening corporate governance practices.
EMS: A Driving Force for ESG Excellence
The integration of EMS with ESG principles creates a synergistic approach that encompasses data-driven monitoring, resource optimization, and stakeholder engagement. This powerful combination empowers manufacturers to make informed decisions that not only reduce their environmental footprint but also enhance social responsibility and strengthen corporate governance.
EMS facilitates a holistic approach to ESG excellence by providing:
-
- Real-time energy consumption monitoring: EMS enables continuous data collection and analysis of energy usage patterns, enabling manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and implement targeted energy-saving measures.
-
- Predictive energy consumption forecasting: Utilizing historical data and advanced algorithms, EMS can predict future energy consumption trends, allowing manufacturers to proactively optimize resource allocation and minimize energy costs.
-
- Identification and rectification of energy losses: EMS proactively detects and quantifies energy losses, facilitating the implementation of corrective actions to prevent wasted energy and reduce operating expenses.
-
- Comprehensive energy consumption analysis: EMS provides granular insights into energy consumption at various levels, including departments, production lines, and individual equipment, enabling data-driven decision-making.
-
- Enhanced employee engagement: EMS promotes a culture of energy conservation and sustainability among employees, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility towards environmental stewardship.
-
- Strengthened corporate governance: EMS implementation demonstrates a company’s commitment to environmental responsibility and good governance practices, enhancing its reputation and attracting socially conscious investors.
The Path Forward for Sustainable Manufacturing
To fully leverage the potential of EMS and achieve ESG excellence, manufacturers should consider the following key recommendations:
-
- Adopt an integrated ESG strategy: Integrate ESG principles into all aspects of business operations, from product development and supply chain management to employee engagement and community involvement.
-
- Embrace technological innovation: Continuously explore and adopt advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT, to enhance energy monitoring, optimize resource usage, and automate sustainability initiatives.
-
- Cultivate a sustainability mindset: Foster a company culture that prioritizes environmental responsibility, social consciousness, and ethical practices among employees at all levels.
-
- Pursue continuous improvement: Regularly review and refine EMS strategies to adapt to evolving environmental challenges, regulatory changes, and stakeholder expectations.
By embracing EMS and adopting these recommendations, manufacturers can position themselves as leaders in ESG excellence, reaping the associated benefits of enhanced brand reputation, improved shareholder value, and a more sustainable future. As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, EMS will remain a critical tool for companies seeking to balance economic growth with environmental stewardship and social responsibility.
Related to this article

Enhancing Production Sustainability with Energy Management Systems
1. The Importance of Production Sustainability In today’s world, where environmental concerns and economic challenges intertwine, the importance of sustainable production patterns and practices cannot

Energy Management System (EMS)
Energy Management System (EMS) Monitor utilities usage in real-time and reduce cost Schedule a Demo They Trusted Us: What is ANT EMS? ANT Energy Management

MES System – Manufacturing Execution System – ANT Solutions
System MES – Manufacturing Execution System 0 % operating time increase 0 % defects quantity reduction 0 % material consumption reduction 0 % changeovers time

